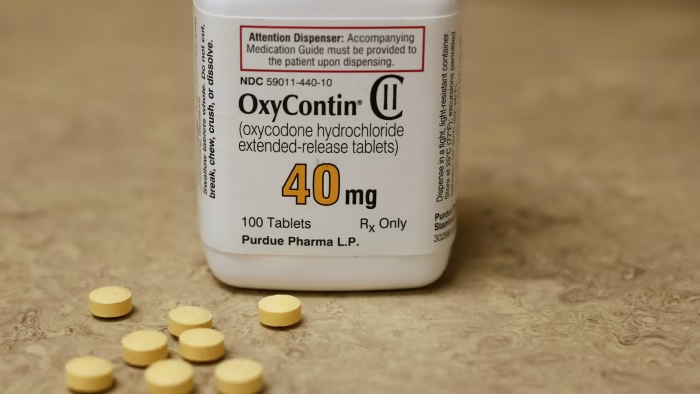
Oxycontin 40mg In Australia, Buy Oxycontin Online In Australia, Safe Delivery To All States With Or Without Prescriptions. Oxycontin 40mg In Australia
Chronic pain affects millions of Australians and poses a significant challenge to daily life and well-being. For those who suffer from severe and persistent pain, OxyContin 40mg has been one of the medications used in pain management. However, recent changes in how this medication is prescribed in Australia have reshaped its use, especially for chronic non-cancer pain.
What is OxyContin 40mg?
OxyContin 40mg is an extended-release form of oxycodone, a strong opioid analgesic. It is designed to provide consistent, long-lasting relief for up to 12 hours, making it useful for people who require continuous pain control throughout the day and night. Oxycontin 40mg In Australia
Because it’s extended-release, OxyContin isn’t used for quick or breakthrough pain—it’s intended for chronic, ongoing pain that other medications may not adequately manage.
How It’s Used in Australia
In Australia, OxyContin 40mg is typically used in very specific circumstances, often when other pain management strategies have not been effective. These include:
Chronic severe pain that does not respond well to non-opioid medications.
Cases where other opioids have not provided sufficient relief.
Pain management in individuals who have already been stabilized on lower doses of oxycodone or other opioids.
Doctors assess each patient individually to determine whether the benefits outweigh the potential risks, particularly with long-term use. Buy Fentanyl Patch Online In Europe
Recent Changes in Opioid Prescribing
There have been significant updates to how opioids like OxyContin are prescribed in Australia, aimed at curbing misuse and improving patient safety. Key changes include:
Restricted Use for Chronic Non-Cancer Pain: OxyContin is now only recommended in cases where non-opioid therapies have been unsuccessful or are unsuitable.
Smaller Prescription Quantities: To minimize leftover medication that could be misused, patients are now prescribed smaller quantities.
Second Opinion Requirements: If a patient requires ongoing opioid therapy for more than 12 months, another healthcare provider must review and approve the treatment plan.
Prescription Monitoring Programs: Doctors and pharmacists now use real-time tracking systems to help prevent overprescribing and identify patients who may be at risk of dependence.
Risks and Considerations
While OxyContin can be a powerful ally in pain relief, it also comes with important risks:
Physical Dependence: Long-term use can lead to the body becoming dependent on the drug.
Tolerance: Over time, the body may require higher doses to achieve the same pain relief.
Addiction and Misuse: The euphoric effects of opioids can lead to misuse in some individuals.
Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, constipation, drowsiness, and dizziness. In some cases, more serious effects like respiratory depression can occur, especially if the medication is misused.
Because of these risks, it’s crucial that patients use OxyContin exactly as prescribed and check in regularly with their healthcare provider.
Alternatives to OxyContin
Many Australians are now exploring non-opioid alternatives and complementary therapies to manage chronic pain. These may include:
Non-Opioid Pain Relievers: Medications like paracetamol or anti-inflammatories are often used as a first line of treatment.
Physical Therapy: Strengthening muscles, improving posture, and gentle exercise can play a big role in managing chronic pain.
Psychological Therapies: Chronic pain often has emotional and mental components. Techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help improve coping mechanisms.
Multidisciplinary Pain Clinics: These clinics offer a holistic approach, combining medical, physical, and psychological care tailored to the individual.
Final Thoughts
OxyContin 40mg remains an important medication in the toolkit for managing chronic pain in Australia—but it’s no longer a first-line treatment. The evolving guidelines reflect a shift toward safer, more balanced pain management strategies that consider the whole person—not just the symptoms.
If you or someone you care for is dealing with chronic pain, it’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to find a treatment plan that works, whether that includes medication like OxyContin or other therapies.
For more information, support, and expert resources, visit AUPainRelief.com.



